TNPSC VAS Syllabus 2022 Check Veterinary Assistant Surgeons Exam Pattern here: The Tamil Nadu Public Service Commission released the TNPSC VAS Exam Syllabus 2023. The officials of TNPSC going to conduct the Tamil Nadu Veterinary Assistant Surgeons Exam 2023 on 15.03.2023. Those eligible candidates who were waiting for TN Assistant Surgeons Syllabus 2023 or TNPSC Veterinary Surgeons Exam Pattern 2023 can download the TNPSC Veterinary Assistant Surgeons Syllabus 2023, Tamilnadu Veterinary Assistant Surgeons Exam pattern 2023 from the official website @ tnpsc.gov.in. For the sake of Aspirants, we had given a TNPSC VAS Syllabus 2023 given this article.

www.tnpsc.gov.in Veterinary Assistant Surgeons Syllabus 2023 – Details
| TNPSC VAS Syllabus & Exam Pattern 2022 | |
| Organization Name | Tamil Nadu Public Service Commission (TNPSC) |
| Post Name | Veterinary Assistant Surgeons (VAS) |
| Exam Name | 15.03.2023 |
| Category | Syllabus |
| Syllabus Status | Available |
| Official site | www.tnpsc.gov.in |
TNPSC VAS Exam Date 2023
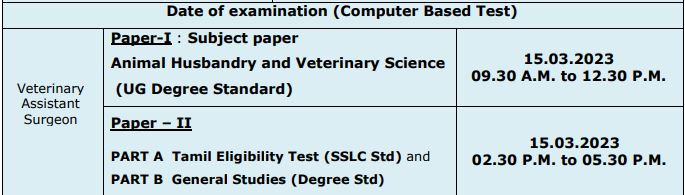
TNPSC VAS Exam Pattern 2023
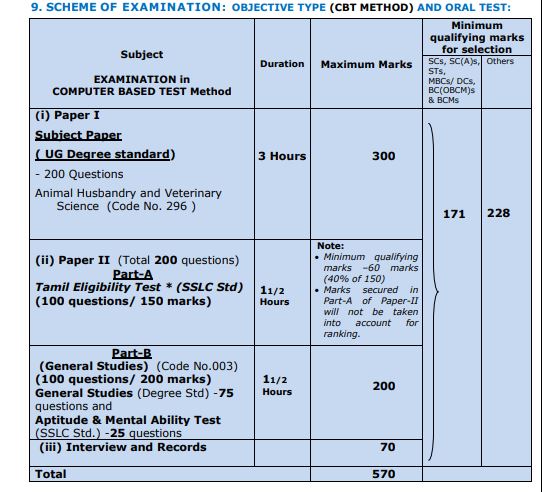
TNPSC VAS Syllabus 2023
ANNEXURE – I (Paper-I)
SYLLABUS FOR EXAMINATION (CBT Method)
CODE NO.296
UNIT – I: GENERAL
Role of livestock and their products in the Indian economy and human health, current livestock programs and policies of State and Nation – Economics of dairy, sheep, goat, poultry, pig, and rabbit farming; constraints to the livestock development programs, common offenses against animals – SPCA, Animal Welfare Board of India, NGOs.
UNIT – II: LIVESTOCK MANAGEMENT
Common terms used in Animal Husbandry – Identification of age of animals – Livestock and poultry breeds and breed characters; housing systems, and requirements of space, ventilation, water, sanitation, and waste disposal. Management of milk, meat, egg, and wool-producing livestock, breeding bulls and draft animals and wild animals in captivity, farm records and their maintenance, systems, and strategies for livestock improvement for enhancing productivity.
UNIT – III: LIVESTOCK NUTRITION
Nutritional terms and definitions – Role of nutrition in health and production; classification and composition of feed and fodders including forest grasses; antinutritional factors and toxins in feeds and fodders; feeding standards and nutrient requirements of different categories of livestock/poultry and computation of rations. Nutritional deficiency and its influence on livestock performance; feed supplements and additives; conservation and preservation of feed and fodders; economic utilization of agro by-products for feeding livestock – Utilisation of unconventional feeds – Wildlife nutrition. Quality control of feed, feed block/baling, By-Pass Proteins and by-pass Fat, Feeding livestock during scarcity, Metabolic disorders in Livestock and Poultry, Processing of feeds and forage to improve nutritive value.
UNIT – IV: LIVESTOCK BREEDING AND GENETICS
Important breeds of cattle, buffalo, sheep, goat, pig, and poultry with special reference to economic characters – Important species of wild animals and their breeding in captivity. Selection of Livestock for production, reproduction and disease resistance traits. Principles of genetics and basis of population genetics, genetic parameters. Nature of DNA and RNA-their models and functions; applications of recombinant DNA technology, cloning and marker Assisted selection and Cytogenetics. Animal breeding policies and programmes in state and Nation.
UNIT – V : VETERINARY ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY AND BIOCHEMISTRY
Gross study of bones, joints and muscles of skeleton Gross study of heart and its conduction system. Gross study of organs of digestive, respiratory urinary and reproductive systems. Digestion, metabolism and absorption of carbohydrates, proteins and fats in simple stomach animals and ruminants – mechanism of respiration. General functions of blood (blood cells, plasma & serum) coagulation, cardiac cycle, Blood circulation, Blood pressure, renal function Hormonal control of Lactogenesis. Environmental factors affecting animal production – Environmental stress on animal performance – Green Houses Gases – Role of ruminants.
UNIT – VI : VETERINARY MICROBIOLOGY, VETERINARY PREVENTIVE MEDICINE
Bacteriology & Mycology: Classification – isolation, identification and culturing of bacteria and fungi -Methods of transmission of infection – Sterilization and disinfection – Antibiogram. Virology: Classification, – cultivation, replication General characteristics of various families of RNA and DNA viruses. Immune system organs, tissues and cells; infection and immunity; type and grade of immunity, serological reactions and modern diagnostic techniques – vaccine. Epidemiology – Concept, Scope, Objectives and Uses. Monitoring and surveillanceepidemiological disciplines. Pathogenesis, clinical signs, differential diagnosis, prevention and control of common bacterial, viral, fungal, rickettsial and parasitic diseases of livestock, poultry and pet animals including wild life species- Regional, endemic, emerging and re-emerging important disease. Allergic skin tests and modern diagnostic techniques.
UNIT – VII : PATHOLOGY AND PARASITOLOGY
Concept and causes of diseases in animals; general principles and procedures of necropsy; collection, preservation and dispatch of morbid materials for laboratory diagnosis, disease investigation; common pathological conditions seen in domestic, wild, zoo and laboratory animals and birds. Vetro-legal implications. Classification of Parasites – Parasite and parasitism in animals; important morphological features, life-cycles, mode of transmission, pathogenesis, diagnosis, chemotherapy and general control measures of parasites associated with disease in animals, birds and zoo animals.
UNIT – VIII : PHARMACOLOGY
Drug action – Pharmacokinetics (absorption, distribution, biotransformation and excretion), Pharmacodynamics – local and general anesthetics. Antibiotics and chemotherapy – Toxicology – Ethnoveterinary practices.
UNIT – IX : VETERINARY CLINICAL MEDICINE, VETERINARY
GYNAECOLOGY AND OBSTETRICS AND VETERINARY SURGERY AND RADIOLOGY
General and special clinical examination, etiology, clinical signs, pathogenesis, diagnosis, prevention and control of metabolic, deficiency diseases. Ethics and jurisprudence in domestic and wild animals. Reproductive physiology; hormones and reproduction; Accidents of gestation, livestock fertility and infertility; artificial insemination; semen characteristics of different species of livestock and cryopreservation. Multiple ovulation and embryo transfer technology in livestock and zoo animals Reproductive disorders and their management. General surgical principles – Pre and post-operative considerations, anesthesia, asepsis and anti-sepsis and sterilization; scope, history and development of veterinary radiology; Imaging pathology of different parts of body-surgical emergencies – Intensive care – Physiotherapy – Diathermy.
UNIT- X : LIVESTOCK PRODUCTS TECHNOLOGY
Ante mortem and Post mortem inspection – Objectives of meat inspection – Abattoir practices, methods of slaughtering and dressing; Meat Inspection Laws, utilization of by products; unsound meat and its disposal; quality control of meat and eggs and their products. Milk: Proximate Composition, milk collection, cooling / chilling and transportation; physio-chemical and nutritional characters of milk and milk products; processing of raw milk and production of market milk. Condensed and dried milk, special milk and Indian Dairy Products – Packaging and storage. Cleaning and sanitization of dairy equipments and plants; role of microorganisms in milk and milk products; legal standards and quality assessment of milk and milk products-role of milk and milk products, meat and egg in human nutrition – Detection of adulterants in milk. Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) in dairy and Hazard analysis in critical control point (HACCP) in dairy Processing. FSSAI laws.


Paper-II (PART – B)
GENERAL STUDIES (DEGREE STANDARD)
CODE NO.003
UNIT-I: GENERAL SCIENCE
(i) Scientific Knowledge and Scientific Temper – Power of Reasoning – Rote Learning vs Conceptual Learning – Science as a tool to understand the past, present and future.
(ii) Nature of Universe – General Scientific Laws – Mechanics – Properties of Matter, Force, Motion and Energy – Everyday application of the Basic Principles of Mechanics, Electricity and Magnetism, Light, Sound, Heat, Nuclear Physics, Laser, Electronics and Communications.
(iii) Elements and Compounds, Acids, Bases, Salts, Petroleum Products, Fertilisers, Pesticides.
(iv) Main concepts of Life Science, Classification of Living Organisms, Evolution, Genetics, Physiology, Nutrition, Health and Hygiene, Human Diseases.
(v) Environment and Ecology.
UNIT-II: CURRENT EVENTS
(i) History – Latest diary of events – National symbols – Profile of States – Eminent personalities and places in news – Sports-Books and authors.
(ii) Polity – Political parties and political system in India-Public awareness and General administration- Welfare oriented Government schemes and their utility, Problems in Public Delivery Systems.
(iii) Geography-Geographical landmarks.
(iv) Economics-Current socio-economic issues.
(v) Science-Latest inventions in Science and Technology.
(vi) Prominent Personalities in various spheres – Arts, Science, Literature and Philosophy.
UNIT-III: GEOGRAPHY OF INDIA
(i) Location – Physical features – Monsoon, Rainfall, Weather and Climate – Water Resources – Rivers in India – Soil, Minerals and Natural Resources – Forest and Wildlife – Agricultural pattern.
(ii) Transport -Communication.
(iii) Social Geography – Population density and distribution- Racial, Linguistic Groups and Major Tribes.
(iv) Natural calamity – Disaster Management – Environmental pollution: Reasons and preventive measures – Climate change – Green energy.
UNIT–IV: HISTORY AND CULTURE OF INDIA
(i) Indus Valley Civilization – Guptas, Delhi Sultans, Mughals and Marathas – Age of Vijayanagaram and Bahmani Kingdoms – South Indian History.
(ii) Change and Continuity in the Socio – Cultural History of India.
(iii) Characteristics of Indian Culture, Unity in Diversity –Race, Language, Custom.
(iv) India as a Secular State, Social Harmony.
UNIT-V: INDIAN POLITY
(i) Constitution of India – Preamble to the Constitution- Salient features of the Constitution- Union, State and Union Territory.
(ii) Citizenship, Fundamental Rights, Fundamental Duties, Directive Principles of State Policy.
(iii) Union Executive, Union Legislature – State Executive, State
Legislature – Local Governments, Panchayat Raj.
(iv) Spirit of Federalism: Centre-State Relationships.
(v) Election – Judiciary in India – Rule of Law.
(vi) Corruption in Public Life – Anti-corruption measures – Lokpal and Lok Ayukta – Right to Information- Empowerment of Women-Consumer Protection Forums, Human Rights Charter.
UNIT-VI: INDIAN ECONOMY
(i) Nature of Indian Economy – Five-year plan models – an assessment – Planning Commission and Niti Ayog.
(ii) Sources of revenue – Reserve Bank of India – Fiscal Policy and
Monetary Policy – Finance Commission – Resource sharing between Union and State Governments – Goods and Services Tax.
(iii) Structure of Indian Economy and Employment Generation, Land Reforms and Agriculture – Application of Science and Technology in Agriculture – Industrial growth – Rural Welfare Oriented Programmes – Social Problems – Population, Education, Health, Employment, Poverty.
UNIT-VII: INDIAN NATIONAL MOVEMENT
(i) National Renaissance –Early uprising against British rule – Indian National Congress – Emergence of leaders –B.R.Ambedkar, Bhagat Singh, Bharathiar, V.O. Chidambaranar Jawaharlal Nehru, Kamarajar, Mahatma Gandhi, Maulana Abul Kalam Azad, Thanthai Periyar, Rajaji, Subash Chandra Bose, Rabindranath Tagore and others.
(ii) Different modes of Agitation: Growth of Satyagraha and Militant Movements.
(iii) Communalism and Partition.
UNIT-VIII: History, Culture, Heritage and Socio-Political Movements in Tamil Nadu
(i) History of Tamil Society, related Archaeological discoveries, Tamil Literature from Sangam Age till contemporary times.
(ii) Thirukkural : (a) Significance as a Secular Literature
(b) Relevance to Everyday Life
(c) Impact of Thirukkural on Humanity
(d) Thirukkural and Universal Values – Equality, Humanism, etc
(e) Relevance to Socio-Politico-Economic affairs
(f) Philosophical content in Thirukkural
(iii) Role of Tamil Nadu in freedom struggle – Early agitations against British Rule – Role of women in freedom struggle.
(iv) Evolution of 19th and 20th Century Socio – Political Movements in Tamil Nadu – Justice Party, Growth of Rationalism – Self Respect Movement, Dravidian Movement and Principles underlying both these Movements, Contributions of Thanthai Periyar and Perarignar Anna.
UNIT–IX: Development Administration in Tamil Nadu
(i) Human Development Indicators in Tamil Nadu and a comparative assessment across the Country – Impact of Social Reform Movements in the Socio – Economic Development of Tamil Nadu.
(ii) Political parties and Welfare schemes for various sections of people – Rationale behind Reservation Policy and access to Social Resources – Economic trends in Tamil Nadu – Role and impact of social welfare schemes in the Socio-Economic Development of Tamil Nadu.
(iii) Social Justice and Social Harmony as the Cornerstones of Socioeconomic Development.
(iv) Education and Health Systems in Tamil Nadu.
(v) Geography of Tamil Nadu and its impact on Economic growth.
(vi) Achievements of Tamil Nadu in various fields.
(vii) e-Governance in Tamil Nadu.
UNIT-X: APTITUDE AND MENTAL ABILITY
(i) Simplification – Percentage – Highest Common Factor (HCF) – Lowest Common Multiple (LCM).
(ii) Ratio and Proportion.
(iii) Simple interest – Compound interest – Area – Volume – Time and Work.
(iv) Logical Reasoning – Puzzles-Dice – Visual Reasoning – Alpha numeric Reasoning – Number Series.