APPSC Horticulture Officer Syllabus 2021 PDF | Check Exam Pattern Here: The officials of the Andhra Pradesh Public Service Commission (APPSC) have released the syllabus and exam pattern for Horticulture Officer Post. Candidiates who have been interested and applied for the exam are now referred to the syllabus and exam pattern from here. For the sake of candidates, We have attached the direct download link below or through the official website – https://psc.ap.gov.in/(S(5pro1c2bpcufvoarvk0czol4))/Default.aspx.
APPSC Horticulture Officer Syllabus 2021 – Details
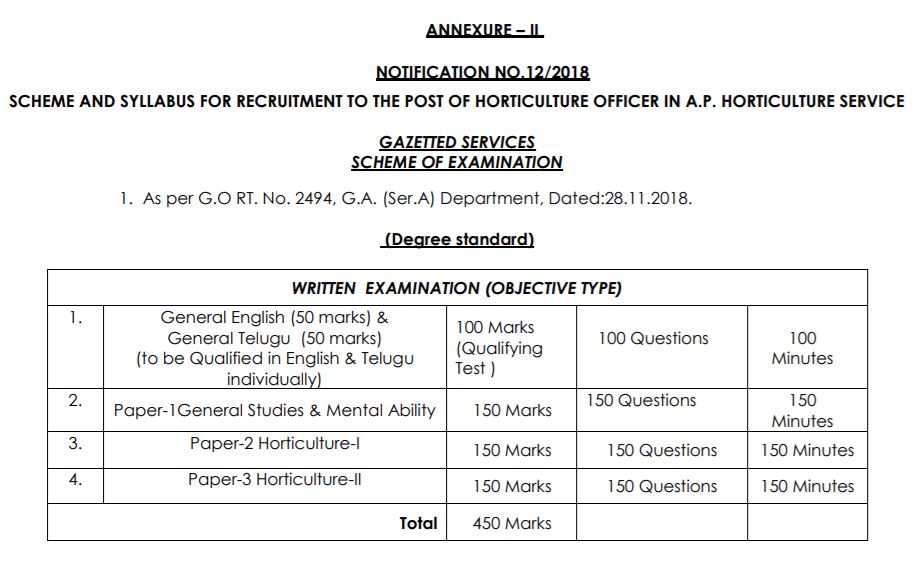
| Download Arunachal Pradesh PSC Horticulture Officer Syllabus 2021 @ appsc.gov.in | |
|---|---|
| Organization Name | Arunachal Pradesh Public Service Commission (Arunachal Pradesh PSC) |
| Post Name | Horticulture Officer |
| Category | Syllabus |
| Syllabus | Released |
| Job Location | Arunachal Pradesh |
| Official website | appsc.gov.in |
APPSC Horticulture Officer Exam Pattern 2021
| Sl. No | Name of the Subjects | No of Marks | No of Questions | Time Duration |
| 1. | General English (50 marks) & General Telugu (50 marks) (to be Qualified in English & Telugu individually) |
100 Marks (Qualifying Test ) |
100 Questions | 100 Minutes |
| 2. | Paper-1General Studies & Mental Ability | 150 Marks | 150 Questions | 150 Minutes |
| 3 | Paper-2 Horticulture-I | 150 Marks | 150 Questions | 150 Minutes |
| 4 | Paper-3 Horticulture-II | 150 Marks | 150 Questions | 150 Minutes |
| Total | 550 Marks |
SCHEME OF EXAMINATION (PRACTICAL TYPE):
| TEST | Duration (Minutes) | Maximum Marks | Minimum qualifying marks | ||
| SC/ST/PH | B.C’s | O.C’s | |||
| Proficiency in Office Automation with usage of Computers and Associated Software | 30 | 50 | 15 | 17.5 | 20 |
The test shall comprise the following four parts:
| Name of the part | Name of the Question to be answered | Marks |
| Part A | Example: Typing a letter/passage/paragraph ( about 100- 150 words ) in MS-Word | 15 |
| Part B | Example: Preparation of a Table/Graph in MS-Excel | 10 |
| Part C | Example: Preparation of PowerPoint Presentations/Slides (Two) on MS-PowerPoint. | 10 |
| Part D | Example: Creation and manipulation of databases. | 10 |
| Part E | Example: Displaying the content of E-mail (Inbox). | 05 |
| Total | 50 |
APPSC Horticulture Officer Syllabus 2021
PAPER-I GENERAL STUDIES AND MENTAL ABILITY
- Events of national and international importance.
- Current affairs- international, national, and regional.
- General Science and its applications to the day to day life Contemporary developments in Science & Technology and Information Technology
- The social-economic and political history of modern India with emphasis on Andhra
Pradesh. - Indian polity and governance: constitutional issues, public policy, reforms and e-governance initiatives with specific reference to Andhra Pradesh.
- Economic development in India since independence with emphasis on Andhra Pradesh.
- Physical geography of Indian sub-continent and Andhra Pradesh.
- Disaster management: vulnerability profile, prevention, and mitigation strategies,
Application of Remote Sensing and GIS in the assessment of Disaster. - Sustainable Development and Environmental Protection
- Logical reasoning, analytical ability, and data interpretation.
- Data Analysis:
a) Tabulation of data
b) Visual representation of data
c) Basic data analysis (Summary Statistics such as mean, median, mode, variance and
coefficient of variation) and Interpretation - Bifurcation of Andhra Pradesh and its Administrative, Economic, Social, Cultural,
Political, and Legal implications/problems.
PAPER-II HORTICULTURE-I
1. FRUIT CROPS
Area, production, importance, use, origin, distribution, botany, classification of varieties, use of rootstocks, high-density planting, climate, soils, planting methods, training and pruning, nutrition, bahar treatment, irrigation scheduling, intercrops, weed control, problems in orchard management, flowering, fruit set, seedlessness irregular bearing, problems in fruit set, harvesting indices, harvesting, preharvest treatments, use of growth regulators, yield, grading, packing for internal and export markets, ripening methods and storage in respect of mango, banana, citrus, grape, pineapple, guava, papaya, and sapota. Physiological disorders in fruit crops.
2. VEGETABLE CROPS
Importance of vegetables in the human diet and national economy. Detailed study regarding origin and distribution, area and production, importance, nutritive value, botany, varieties, soil and climatic requirements, seed treatment, seed sowing/nursery raising, transplanting, nutrition, irrigation, intercultural operations, physiological disorders, harvest indices, harvesting, post-harvest handling, curing, storage and usage of plant growth regulators in vegetable crops like tomato, brinjal, chillies, sweet pepper, potato, okra, cucurbitaceous crops like cucumber, pumpkin, ridge gourd, snake gourd, bitter gourd, bottle gourd, melons like watermelon and must melon, leguminous vegetables like cluster bean, French bean, Dolichos bean, pea and broad bean, cole crops like cabbage, cauliflower and knolkhol, root crops like radish, carrot, beetroot and turnip, bulb crops like onion and garlic, tuber crops like sweet potato, tapioca, amorphophallus, colocasia, Dioscorea and yam, leafy vegetables like amaranthus, palak, Roselle, perennial vegetables like drumstick, coccidia and murraya.
3. COMMERCIAL FLORICULTURE, ORNAMENTAL GARDENING, AND LANDSCAPE ARCHITECTURE
Area, production, importance, use, origin, distribution, classification of varieties, propagation, environmental factors affecting growth and flowering, soils, nutrition, irrigation, weeding, special techniques of production such as controlling growth and production of flowers, use of growth regulators, harvesting, postharvest handling, an extension of shelf life of flowers of commercial flower crops such as rose, chrysanthemum, jasmine, carnations, gladiolus, anthurium, tuberose, china aster, marigold, Cassandra and gerbera. Need for aesthetic planning, places suitable for aesthetic planning-towns, cities, villages, schools, temples, roadside, parks, ghats of rivers and canals, platforms, railway lines, public and private buildings, institutes, and places of worship. Ornamental trees, shrubs climbers, cacti, succulents are used in aesthetic or landscape gardening. Principles of garden designs, types of gardens-Japanese, English, and Moghul gardens. Various features of gardens such as paths, garden walls, fencing, steps, edges, hedges, arches, pergolas, shrubbery, topiary, rockery, flower beds, lawns, fountains, statues, water garden, conservatory, and glass or greenhouse. Indoor plants, and their management.
Flower arrangement – principles, styles, containers, and holding solutions.
Bonsai – culture, and art of making.
4. MEDICINAL, AROMATIC, SPICES, CONDIMENT, AND PLANTATION CROPS
Origin, importance, export potential, varieties, climate, soil requirements, propagation
and planting, and aftercare, mulching, irrigation, training, pruning, harvesting, yield, and post-harvest handling, curing, and processing practices, storage methods, and distillation of
essential oils of the following crops. Medicinal Plants Aloe, amla(aonla), stevia, ashwagandha, Dioscorea, opium poppy, sarpagandha, steroids bearing solanum, Phyllanthus amarus, chakramani, madhunasaini, sweet flag, Catharanthus, roses, isabgol, foxglove, belladonna, senna, Tinospora, annatto, coleus, Safed Musli, and asparagus. Aromatic Crops Citronella, lemon grass, palmarosa, vettiver, geranium, davana, mints, lavender and vanilla. Spices and condiments Turmeric, ginger, coriander, fenugreek, cardamom, pepper, cinnamon, clove, nutmeg, and cumin. Plantation Crops Coconut, cashew nut, oil palm, betel vine, coffee, tea, cacao, areca nut, and rubber.
5. DRYLAND HORTICULTURE AND WATERSHED MANAGEMENT
Dryland horticulture farming, introduction, definition, dry climate, and their classifications with reference to India in general and Andhra Pradesh in particular. Importance of horticultural crops in dryland, yield potential of agriculture, and horticultural crops in drylands. Fruits and vegetable crops are suitable for dryland farming. Adaptive features of dryland fruit crops for drought and salinity.
Watershed management, objectives, approaches, steps in watershed development planning, land use capability, classification, soil and rainwater conservation, water harvesting measures in the watershed areas. Problems and prospects under watershed. Alternate water use system.
Cultural practices like planting, training, pruning, nutrition and water management, and harvesting of important dry land fruits viz., ber, pomegranate, custard apple, phalsa, fig,
aonla, jamun and tamarind.
6. Post Harvest Management of Horticultural Crops
Importance of post-harvest technology in Horticultural crops. Maturity indices, harvesting, handling, grading of fruits, vegetables, cut flowers, plantation crops, medicinal and aromatic plants. Pre-harvest factors affecting quality, factors responsible for deterioration of horticultural produce, physiological and biochemical changes, hardening and delaying ripening process. Post-harvest treatments of horticultural crops. Quality parameters and specifications. Structure of fruits, vegetables, and cut flowers related to physiological changes after harvest. Methods of storage for local market and export, packaging methods and types of packages, recent advances in packaging. Types of containers and cushioning materials, vacuum packaging, cold storage, poly shrink packaging, grape guard packing treatments. Modes of transport.
7. PRESERVATION OF FRUITS AND VEGETABLES
Importance and scope of fruit and vegetable preservation in India. Principles of preservation by heat, low temperature, chemicals, and various methods of preservation Selection of site for processing, processing unit layout, and precautions for hygienic conditions of the unit. Preservation of fruits and vegetables through canning, bottling, freezing, dehydration, drying, sugar, chemicals, salts, vinegar, ultraviolet, and ionizing radiations.
Microorganisms associated with spoilage of fruit and vegetable products. Spoilage of canned products-hydrogen swell, flipper, dent, leaker, etc., Biochemical changes associated with spoilage of fruit and vegetable products. Preservatives and colors are permitted and prohibited in India.
8. FARM POWER AND MACHINERY
Farm power in A.P and India – Sources, I.C engines, classification, Tractors – Types and uses, selection of tractor and cost of tractor power. Electric motors – types, Tillage implements – primary secondary tillage drawn implements. Seed cum fertilizer drills, planters. Grafting and pruning tools and equipment. Implements, tools, and equipment for intercultural operations. Plants protection equipment – harvesting equipment – soil conservation equipment.
Different kinds of equipment are used in processing. Preparation of jams, jellies, marmalades, candies, crystallized and glazed fruits, preserves, chutneys, pickles, ketchup, sauce, puree, syrups, juices, squashes, and cordials. Government policy on import and export of processed fruits, food laws. Quality control of processed products.
9. GREENHOUSE MANAGEMENT OF HORTICULTURAL CROPS
Importance uses scope, and production of horticultural crops in the greenhouse. Status and development of greenhouse production of horticultural crops in the world and India. Development, constraints, research needs, and future of the protected culture of horticultural crops in India and A.P. Points to be considered before establishing a greenhouse. Types of greenhouses, classification of greenhouses based on the shapes, the material used, utility, and cladding material used. Size and arrangement of greenhouses and characteristics of various greenhouse cladding materials, greenhouse benches, etc.,
Management of light, temperature (greenhouse heating and cooling), CO2, and relative humidity inside the greenhouse. Various types of growing media used and their suitability for different horticultural crops. Preparation of growing media and its pasteurization. Management of nutrients through fertigation. Detailed production technology in respect of tomato, cucumber, rose, carnation, gerbera, chrysanthemum, and anthurium under greenhouse/polyhouse.
PAPER-III HORTICULTURE-II
1. FUNDAMENTALS OF HORTICULTURE:
Definition, the importance of horticulture in terms of economy, production, and employment generation. Nutritional value of horticultural crops. Divisions of horticulture and their importance. Horticultural stations in Andhra Pradesh. Horticultural zones of India and Andhra Pradesh.
Temperature, light, humidity, rainfall, and soil requirements for horticultural crops. Selection of site for establishing an orchard, orchard plan, systems of planting, and establishment of an orchard. Importance, scope, and practicing of organic farming in horticultural crop production. Soil and climate for horticultural crops. Vegetable gardens – nutrition and kitchen gardens and other types of gardens.
Nutrition of horticultural crops – assessment of nutritional requirements based on soil, tissue analysis, and field experiments. Identification of deficiency symptoms of various nutrients and methods of nutrient application. Assessment of irrigation requirements for different horticultural crops and different methods of irrigation. Pruning and training, their
objectives and methods. Pollination and fruit set, problems and requirements, flower and fruit drop, stages, causes, and remedial measures. Fruit thinning, objectives, advantages, and disadvantages. Unfruitfulness, reasons, and remedial measures. Use of growth regulators in horticulture. Cropping systems, intercropping, multi-tier cropping, mulching, bearing habits, factors influencing fruitfulness and unfruitfulness. Rejuvenation of old orchards, top working, framework.
2. PLANT PROPAGATION AND NURSERY MANAGEMENT :
Introduction, principles, and classification of plant propagation methods. Selection of site for commercial nursery. Ecological and economic factors. Plant propagation structures, containers, and media.
Sexual propagation and its importance. Seed dormancy, Seed germination, the process of seed germination. Factors affecting seed germination and pre-germination treatments and viability tests.
Asexual (vegetative) propagation and its importance. Various methods of Asexual (vegetative) propagation like cottage, layering, budding, grafting, and factors responsible for their success. Different types among cottage, layering, budding, grafting methods followed in the propagation of different horticultural crops. Role of rootstocks, selection and maintenance of mother trees (scion bank), scion–stock relationships, bud wood certification, propagation through specialized structures. Nursery registration act. Importance of micropropagation of plants. Types of aseptic cultures. Types of media, preparation of media and inoculation of explants, establishment, subculture, and rooting of explants.
3. PLANT PHYSIOLOGY :
Physiological changes during seed development, germination, and seed dormancy. Seed viability and seed vigor. Photosynthesis – importance, factors affecting photosynthesis. Light and dark reactions – C3, C4, and CAM pathways. Significance and differences. Photorespiration and its significance. Respiration and its significance. Nomenclature and classification of plant growth substances. History, occurrence, distribution, mode of action, movement, mechanism, and function of auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, ethylene, inhibitors, retardants, phenolic substances, and morphactins.
Role of plant growth regulators in plant propagation, seed and bud dormancy, juvenility, maturity and senescence, flowering, pollination, fruit set including parthenocarpy, fruit growth, fruit drop and fruit ripening (climacteric and non-climacteric), and fruit color development, tuber, and bulb formation, and sex expression and extension of shelf life in fruits, vegetables, and flowers.
4. ENTOMOLOGY:
Commonly occurring pests in horticultural crops – distribution, host range, nature of damage, symptoms, and control measures. The life cycle of insect pests, nematodes, etc., Integrated pest management.
5. PATHOLOGY :
Commonly occurring diseases in horticultural crops – host range, etiology, symptoms, and control measures. The life cycle of bacteria, fungal parasites, viruses, etc., Integrated disease management.
6. SOIL SCIENCE:
Soil texture – classes. Soil structure – classification. Soil PH, the importance of soil PH on nutrient availability. Soil organic matter – sources, humus formation, C: N ratio, and its importance. Soil fertility and productivity. Essential and beneficial elements, criteria of essentiality. Primary secondary, micronutrients and their functions, deficiency symptoms, occurrence in horticultural crops, corrective measures. Factors affecting their availability.
Classification of manures and fertilizers and their differences. Commercial fertilizers, simple, compound, and complex fertilizers, fertilizers mixtures. Biofertilizers. Integrated nutrient management for horticultural crops. Fertilizer control order.
7. INTRODUCTORY AGROFORESTRY :
Agro forestry-introduction, the status of Indian forests, role in Indian Farming Systems. Definition Branches of Forestry. Principles and practices, classification of Agroforestry systems-inter cropping-Home garden-Types of coconut-based cropping system-planning for Agroforestry constraints, diagnosis and design methodology, selection of tree species for agroforestry.
Agroforestry projects-national, overseas, MPTs – their management practices economics of cultivation – Sisso, Acacia catechu, A.nilotica (Babul), Bez(Z. mauritiana). Grewia, Subabul, Tamarind, Eucalyptus, Teak, Casuarina, Red sander, Neem, Soapnut, Aonla, Morus, Bamboo, biodiesel trees-Jatropha, Pongamia, Simarouba. The distinction between agroforestry and social forestry objectives, the scope of social forestry. Hortipastoral system – pastures suitable under dryland conditions.
8. EXTENSION EDUCATION:
Formal and informal education. Teaching-learning process, principles of learning. Commutation – components. Classification of Audiovisual aids. Transfer of technology programmers – KVK, TAR – IVLP, ATIC, NHM, APMIP, DWCRA, ANTWA, DAATC. Extension reforms – ATMA, SREP, PRA, different tools of PRA.
9. ORGANIC FARMING IN HORTICULTURAL CROPS :
Introduction, concept, relevance in the present context, Organic production requirements, Biological intensive nutrient management-Organic manures, vermicomposting, green manuring, compost pits, recycling of organic residues, bio-fertilizers, soil improvement, and amendments: Integrated diseases and pest management use of biocontrol agents, biopesticides, pheromones, trap crops bird perches, weed management. Quality considerations, certification, labeling and accreditation processors, marketing, exports. International and National Policies in promotion of Organic farming.
(PRACTICAL TYPE):
PART-A (Word):
Create and save a document using MS WORD
- Deletion of Character, Word, line, and block of text
- Undo and redo the process
- Moving, Copying, and renaming
Format the Text document
- Character formatting
- Paragraph formatting
- Page formatting
Spell check the document
- Finding and Replacing of text
- Bookmarks and Searching for a Bookmarks
- Checking Spelling and Grammar automatically
- Checking Spelling and Grammar using Dictionary
Print the document
- Print Preview
- Print Dialog box
Mail Merge in Ms-word
- Create main document and data file for mail merging
- Merging the files
- From letters using mail merging
- Mailing labels using mail merging
Table creation in Ms-word
- Create a table in the document
- Add row, column to a table
- Changing column width and row height.
- Merge, split cells of the table.
- Use formulae in tables.
- sorting data in a table.
- formatting a table.
Ability to type on Qwerty keyboard of Computer at a speed of at least equivalent to 30 Words per 1 minute (Lower typewriting test).
PART-B (Excel):
- Create and save a new workbook in Excel
- Entering Data into Worksheet
- Editing data of Worksheet
- Formatting the text in the cells
- Formatting the numbers in the cells.
- Formatting cells.
- Copying format of the cell along with data format.
- Changing the height and width of cells.
- Freezing Titles, splitting the screen
- Enter formulae for calculation in the cells.
- Copying the formula over a range of cells.
- Inserting built-in functions into the cells.
- Create graphs for the data using Chart Wizard.
- Format graphs in Excel.
- Printing of worksheet.
PART-C (POWERPOINT):
- Create and save a new presentation using MS PowerPoint
- The layout of the opening screen in PowerPoint
- The toolbars in MS PowerPoint
2. Choose Auto Layout for a new slide.
3. Insert text and pictures into a blank slide.
4. Insert new slides into the presentation.
5. Apply slide transition effects.
6. Slide show.
7. Set animation to text and pictures in a slide
8. Set the sounds, order, and timing for animation.
PART-D (ACCESS):
Creation and manipulation of databases
PART-E (INTERNET):
- Browse the Net using Browser software (Internet Explorer, Mozilla Firefox, Google
Chrome etc.,). - Search the Web using Search Engines.
- Create an E-mail account.
- Send and receive E-mail.
- E-commerce transactions.
- Web content uploading.
- Ability to operate Mac OS / pages / keynote / Numbers
Download APPSC Horticulture Officer Syllabus 2021 – Click Here (Available)