TNPSC DEO Syllabus 2023 Check Group I C Services Exam Pattern Here: The Tamil Nadu Public Service Commission (TNPSC) released the TNPSC DEO Syllabus 2023 and Tamil Nadu DEO Exam Pattern 2023. The officials of TNPSC going to conduct the District Educational Officer Exam 2023. Those eligible candidates who were waiting for TNPSC Group I Civil Services Exam Syllabus 2023 and TNPSC Group I Civil Services Exam Pattern 2023 can download it from the official website @ https://www.tnpsc.gov.in/. For the sake of Aspirants, we had given a Tamil Nadu Group I DEO Syllabus and Exam Pattern 2023 below this section.

www.tnpsc.gov.in Group I DEO Syllabus 2023 – Overview
| TNPSC DEO Group I Civil Services Exam Pattern 2023 Download | |
| Organization Name | Tamil Nadu Public Service Commission (TNPSC) |
| Post Name | Group I C Services District Educational Officer (DEO) |
| No.of. Vacancies | 11 Posts |
| Prelims Exam Date | 09.04.2023 |
| Category | Syllabus |
| Syllabus Status | Available |
| Official Website | www.tnpsc.gov.in |
TNPSC Group I DEO Exam Pattern 2023
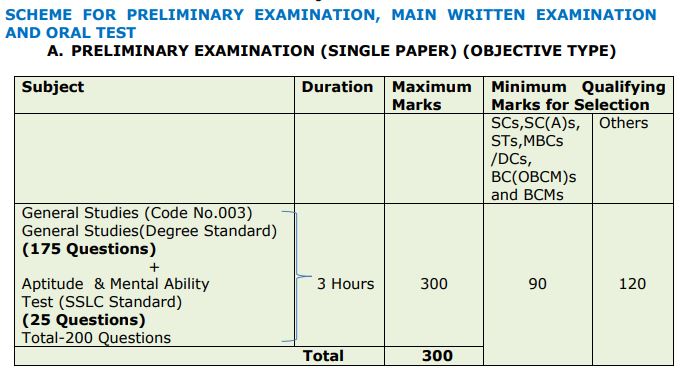
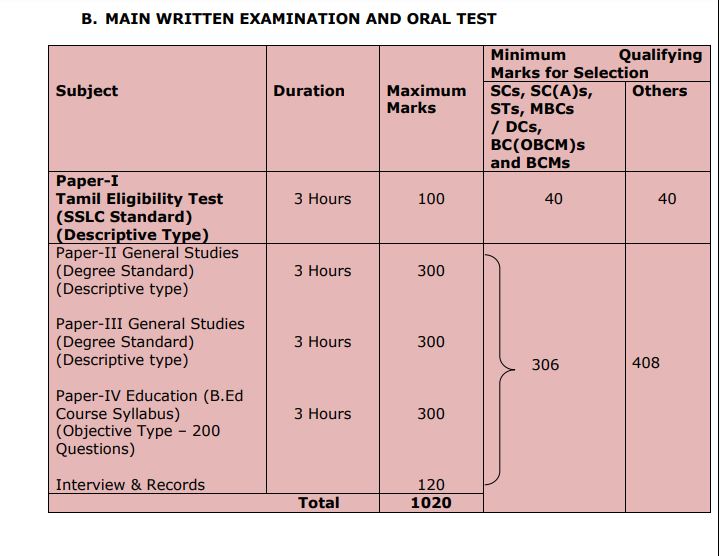
TNPSC DEO Preliminary and Mains Exam Date & Time 2023

TNPSC Group I DEO Prelims & Mains Exam Syllabus 2023
Syllabus for Preliminary Examination
General Studies (Degree Standard) Subject Code: 003
UNIT-I: GENERAL SCIENCE
(i) Scientific Knowledge and Scientific temper – Power of Reasoning – Rote Learning Vs Conceptual Learning – Science as a tool to understand the past, present, and future.
(ii) Nature of Universe – General Scientific Laws – Mechanics
Properties of Matter, Force, Motion, and Energy – Everyday
application of the basic principles of Mechanics, Electricity and
Magnetism, Light, Sound, Heat, Nuclear Physics, Laser, Electronics, and Communications.
(iii) Elements and Compounds, Acids, Bases, Salts, Petroleum
Products, Fertilizers, Pesticides.
(iv) Main concepts of Life Science, Classification of Living Organisms, Evolution, Genetics, Physiology, Nutrition, Health and Hygiene, and Human diseases.
(v) Environment and Ecology
UNIT-II: CURRENT EVENTS
(i) History – Latest diary of events – National symbols – Profile of States – Eminent personalities and places in the news – Sports Books and authors.
(ii) Polity – Political parties and political system in India – Public awareness and General administration – Welfare-oriented Government schemes and their utility, Problems in Public Delivery Systems.
(iii) Geography – Geographical landmarks.
(iv) Economics – Current socio-economic issues.
(v) Science – Latest inventions in Science and Technology.
(vi) Prominent Personalities in various spheres- Arts, Science, Literature, and Philosophy
UNIT- III: GEOGRAPHY OF INDIA
(i) Location – Physical features – Monsoon, Rainfall, Weather and
Climate – Water Resources – Rivers in India – Soil, Minerals and
Natural resources – Forest and Wildlife – Agricultural pattern.
(ii) Transport – Communication.
(iii) Social Geography – Population density and distribution – Racial, Linguistic Groups and Major Tribes.
(iv) Natural calamity – Disaster Management – Environmental pollution: Reasons and preventive measures – Climate change – Green energy.
UNIT– IV: HISTORY AND CULTURE OF INDIA
(i) Indus valley civilization – Guptas, Delhi Sultans, Mughals, and Marathas – Age of Vijayanagaram and Bahmani Kingdoms -South Indian history.
(ii) Change and Continuity in the Socio-Cultural History of India.
(iii) Characteristics of Indian culture, Unity in diversity – Race, language, custom.
(iv) India as a Secular State, Social Harmony.
UNIT-V: INDIAN POLITY
(i) Constitution of India – Preamble to the Constitution – Salient features of the Constitution – Union, State, and Union Territory.
(ii) Citizenship, Fundamental rights, Fundamental duties, Directive
Principles of State Policy.
(iii) Union Executive, Union legislature – State Executive, State Legislature – Local Governments, Panchayat Raj.
(iv) Spirit of Federalism: Centre – State Relationships.
(v) Election – Judiciary in India – Rule of law.
(vi) Corruption in public life – Anti-corruption measures – Lokpal and Lokayukta – Right to Information – Empowerment of women –
Consumer protection forums, Human rights charter.
UNIT-VI: INDIAN ECONOMY
(i) Nature of Indian economy – Five-year plan models – an
assessment – Planning Commission and Niti Ayog.
(ii) Sources of revenue – Reserve Bank of India – Fiscal Policy and
Monetary Policy – Finance Commission – Resource sharing
between Union and State Governments – Goods and Services Tax.
(iii) Structure of Indian Economy and Employment Generation, Land reforms and Agriculture – Application of Science and Technology in Agriculture – Industrial growth – Rural Welfare Oriented Programmes – Social problems – Population, Education, Health, Employment, Poverty.
UNIT-VII: INDIAN NATIONAL MOVEMENT
(i) National Renaissance – Early uprising against British rule – Indian National Congress – Emergence of leaders – B.R.Ambedkar, Bhagat Singh, Bharathiar, V.O.Chidambaranar, Jawaharlal Nehru, Kamarajar, Mahatma Gandhi, Maulana Abul Kalam Azad, Thanthai Periyar, Rajaji, Subash Chandra Bose, Rabindranath Tagore, and others.
(ii) Different modes of Agitation: Growth of Satyagraha and Militant Movements.
(iii) Communalism and partition.
UNIT- VIII: History, Culture, Heritage and Socio-Political Movements in Tamil Nadu
(i) History of Tamil Society, related Archaeological discoveries, Tamil Literature from Sangam age till contemporary times.
(ii) Thirukkural :(a) Significance as a Secular literature
(b) Relevance to Everyday Life
(c) Impact of Thirukkural on Humanity
(d) Thirukkural and Universal Values – Equality, Humanism, etc
(e) Relevance to Socio – Politico-Economic affairs
(f) Philosophical content in Thirukkural
(iii) Role of Tamil Nadu in freedom struggle – Early agitations against British Rule – Role of women in the freedom struggle.
(iv) Evolution of 19th and 20th Century Socio-Political movements in Tamil Nadu – Justice Party, Growth of Rationalism – Self Respect Movement, Dravidian Movement and Principles underlying both these movements, Contributions of Thanthai Periyar and Perarignar Anna.
UNIT – IX: Development Administration in Tamil Nadu
(i) Human Development Indicators in Tamil Nadu and a comparative assessment across the Country – Impact of Social Reform movements in the Socio-Economic Development of Tamil Nadu.
(ii) Political parties and Welfare schemes for various sections of people – Rationale behind Reservation Policy and access to Social Resources – Economic trends in Tamil Nadu – Role and impact of social welfare schemes in the Socio-Economic Development of Tamil Nadu.
(iii)Social Justice and Social Harmony as the Cornerstones of Socio-Economic development.
(iv) Education and Health systems in Tamil Nadu.
(v)Geography of Tamil Nadu and its impact on Economic growth.
(vi) Achievements of Tamil Nadu in various fields.
(vii) E-governance in Tamil Nadu.
UNIT-X: APTITUDE AND MENTAL ABILITY (S.S.L.C STANDARD)
(i) Simplification – Percentage – Highest Common Factor (HCF) – Lowest Common Multiple (LCM).
(ii) Ratio and Proportion.
(iii) Simple interest – Compound interest – Area – Volume – Time and Work.
(iv) Logical Reasoning – Puzzles – Dice – Visual Reasoning – Alphanumeric Reasoning – Number Series.


Mains Exam Syllabus
Paper – II General studies
UNIT – I: Modern history of India and Indian culture
The advent of European invasion- Expansion and consolidation of British rule – Effect of British rule on socio-economic factors – Social reforms and religious movements – India since independence – Characteristics of Indian culture – Unity in diversity – race, colour, language, custom – India – a secular state – Organizations for fine arts, dance, drama, music – Growth of rationalist, Dravidian movement in Tamil Nadu – Political parties and populist schemes – National renaissance – Early uprising against British rule – 1857 Revolt – Indian National Congress – The emergence of national leaders – Gandhi, Nehru, Tagore, Netaji – Growth of militant movements -Different modes of agitations – Era of different Acts & Pacts – World war & final phase struggle – Communalism led to partition – Role of Tamil Nadu in freedom struggle – Rajaji, VOC, Periyar, Bharathiar & Others.
UNIT – 2 General Mental Ability
Conversion of information to data – Collection, compilation and presentation of data – Tables, graphs, diagrams – Parametric representation of data -Analytical interpretation of data – School arithmetic – Percentage – Highest Common Factor(HCF) – Lowest Common Multiple (LCM) – Ratio and Proportion – Simple interest – Compound interest – Area – Volume – Time and Work – Probability – Information technology – Basic terms, Communications – Application of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) – Decision-making and problem-solving – Basics in Computers/Computer terminology
UNIT – 3: Role and impact of science and technology in the development of India and Tamil Nadu
Nature of universe – General scientific laws – Scientific instruments – Inventions and discoveries – National Scientific laboratories – Science glossary – Physical quantities, standards and units – Mechanics and properties of matter – Force, motion and energy – Heat, light and sound – Magnetism, electricity and electronics – Atomic and nuclear physics – Astronomy and space science – Elements and compounds – Acids, bases and salts – Oxidation and reduction – Carbon, nitrogen and their compounds – Natural disasters – safeguard measures – Chemistry of ores and metals – Fertilizers, pesticides, insecticides – Biochemistry and biotechnology – Polymers and plastics – Electrochemistry – Main concepts of life science – The cell -the basic unit of life – Classification of living organism – Nutrition and die tics – Respiration – Excretion of metabolic waste – Bio – communication – Blood and blood circulation – Endocrine system- Reproductive system- Animals, plants and human life – Govt. policy /organizations on Science and Technology – Role, achievement & impact of Science and Technology – Energy – self-sufficiency – oil exploration – Defence Research Organization – Ocean research and development -Genetics – the science of heredity – Environment, ecology, health and hygiene, Biodiversity and its conservation – Human diseases, prevention and remedies – Communicable diseases and non – communicable diseases – Alcoholism and Drug abuse – Computer science and advancement – Genetic Engineering – Remote sensing and benefits.
Mains Exam Paper III
General Studies
UNIT – I – Indian polity and emerging political trends across the world affecting India and the Geography of India
Indian polity – Constitution of India – Preamble to the constitution – Salient features of constitution – Union, state and territory – Citizenship – rights and duties – Fundamental rights – Directive principles of state policy – Fundamental duties – Human rights charter – Union executive – Union legislature – parliament – State executive – State legislature – assembly – Status of Jammu & Kashmir – Local government – panchayat raj – Indian federalism – center state relations – Judiciary in India – Rule of law/Due process of law – Emergency provisions – Civil services in India – Administrative Challenges in a welfare state – Complexities of district administration – Elections – Election Commission Union and State – Official language and Schedule – VIII – Amendments to constitution – Schedules to constitution.
a. Emerging political trends across the world affecting India Foreign Affairs with special emphasis on India’s relations with neighbouring countries and in the region -Security and defence related matters – Nuclear policy, issues and conflicts- The Indian Diaspora and its contribution to India and the world.
b. Geography of India Earth and universe – Solar system – Atmosphere, hydrosphere, lithosphere – Monsoon, rainfall, weather and climate – Water resources – rivers in India – Soil, minerals & natural resources – Natural vegetation – Forest & wildlife – Agricultural pattern, livestock & fisheries – Transport & communication – Centers of trade, commerce & art – Social geography – population – density and distribution – Natural calamities – disaster management – Bottom topography of Indian ocean, Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal – Climate change – impact and consequences – mitigation measures – Pollution Control

3. Administration of Union and States with special reference to Tamil Nadu: State government organization – structure, functions and control mechanism – District administration -role in people’s welfare-oriented programmes – Industrial map of Tamil Nadu – the role of state government -Public Services – the role of recruitment agencies – State finance – resources, budget and financial administration – Use of IT in administration – e-governance in the State -Natural calamities -strategic planning in the State – Social welfare – Government-sponsored schemes with reference to Tamil Nadu – Union government organization – structure, functions and control mechanism – Relationship between State and Union – Industrial map of India – the role of Union government – Public Services – the role of recruitment agencies in Union Government – Union finance – resources, budget and financial administration – Use of IT in administration – e- governance in Union Government – Natural calamities -strategic planning by the Union – Social welfare – government-sponsored schemes by the Government of India.
Paper IV B.Ed Courses
Current trends and challenges in Education- Innovation in Education – Education Psychology -Philosophy in Education, Eastern and Western Education – Education Sociology – Scheme S.S.A. & RMSA – Curriculum – Measurements and Evaluation – Human Rights & R.T.E. Act – Learner /Learning – Inclusive Education – Information and Communication Technology – Education Management – Gender Sensitization – Environmental Education – Vocational Guidance – Health and Physical Education – Distance and Open Learning – Outreach Programme – Committee and Commissions in Education – Basic concept of Psychology.